Remediation
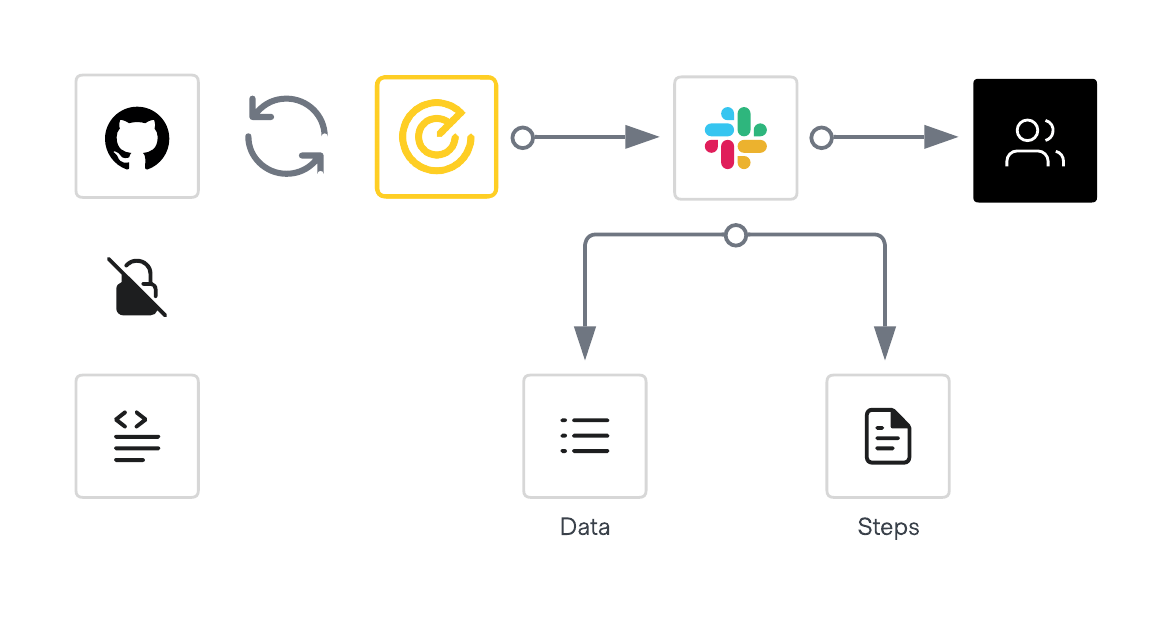
Beyond secret detection, Vault Radar has a suite of features to help teams efficiently remediate issues found by Radar.
The features are:
- Notification integrations
- Resource based roles
- Remediation recommendations
- Remediation actions
Notification integrations allow Vault Radar administrators to notify development teams when there is an event that needs remediation. We support integrations with:
- Microsoft Teams
- Jira
- ServiceNow
- Splunk
- PagerDuty
- Slack
Vault Radar administrators can also grant developer access to specific resources for least-privileged access at the group level.
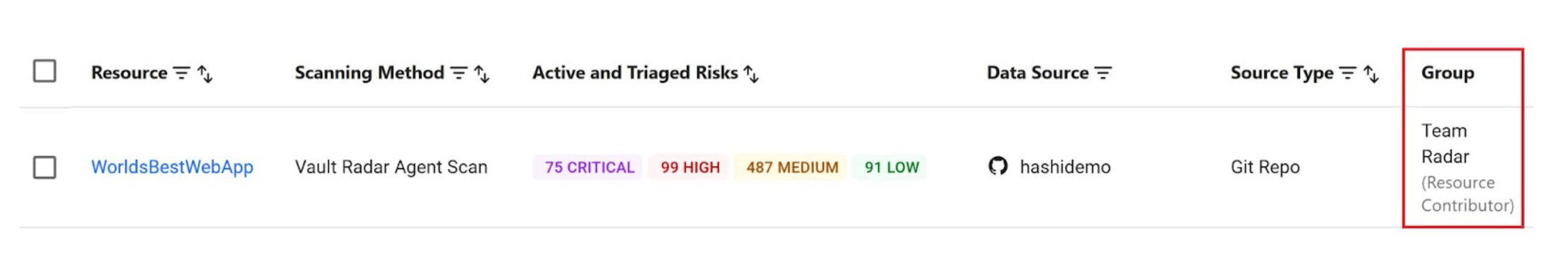
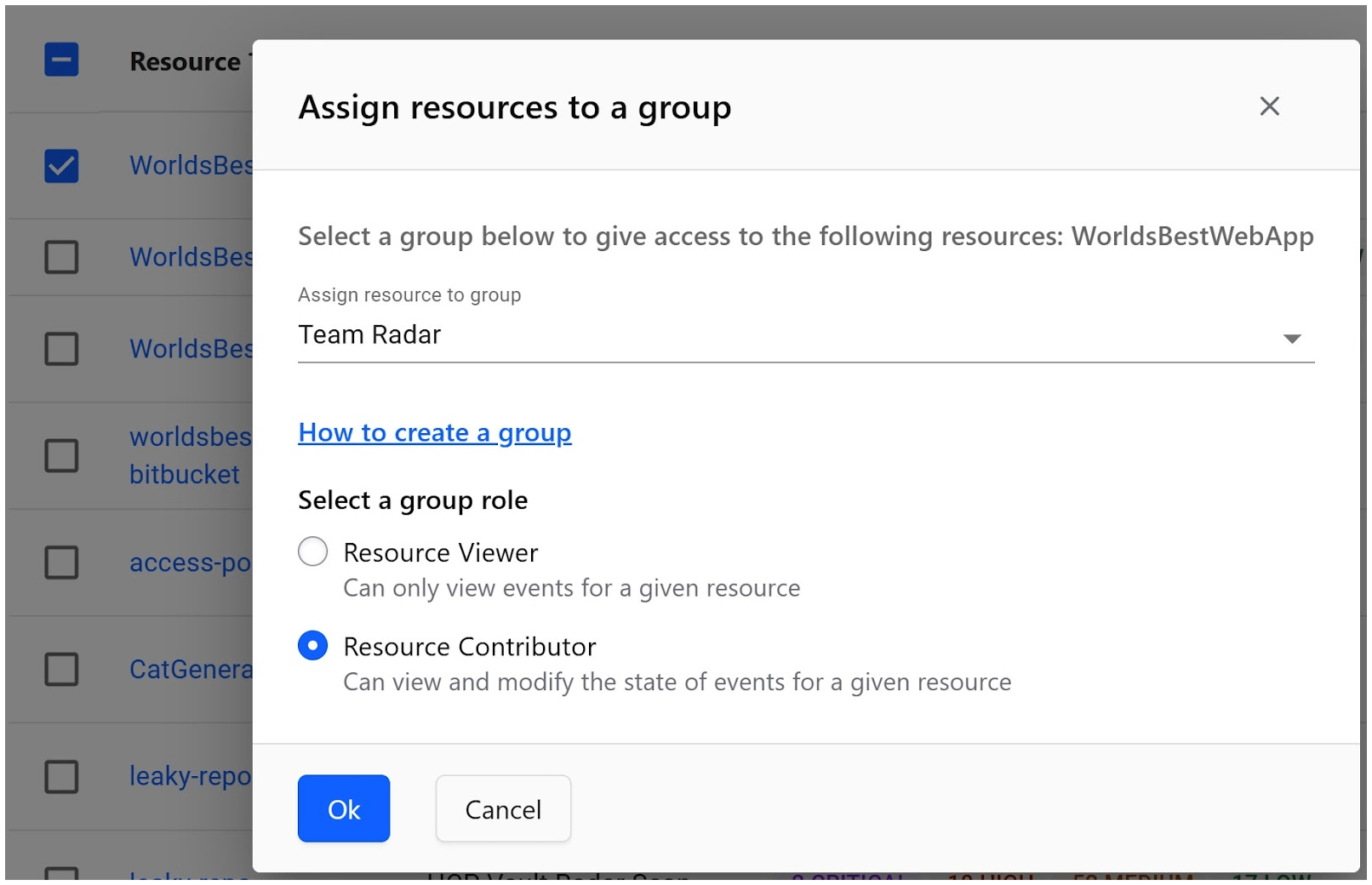
Create groups at the HCP organization level, and then assign them to one or more data sources or repositories with Resource Contributor or Viewer roles. While the Resource Viewer role can only view information about a risk, a Resource Contributor can view and modify the state of a risk, possibly applying remediation to it.
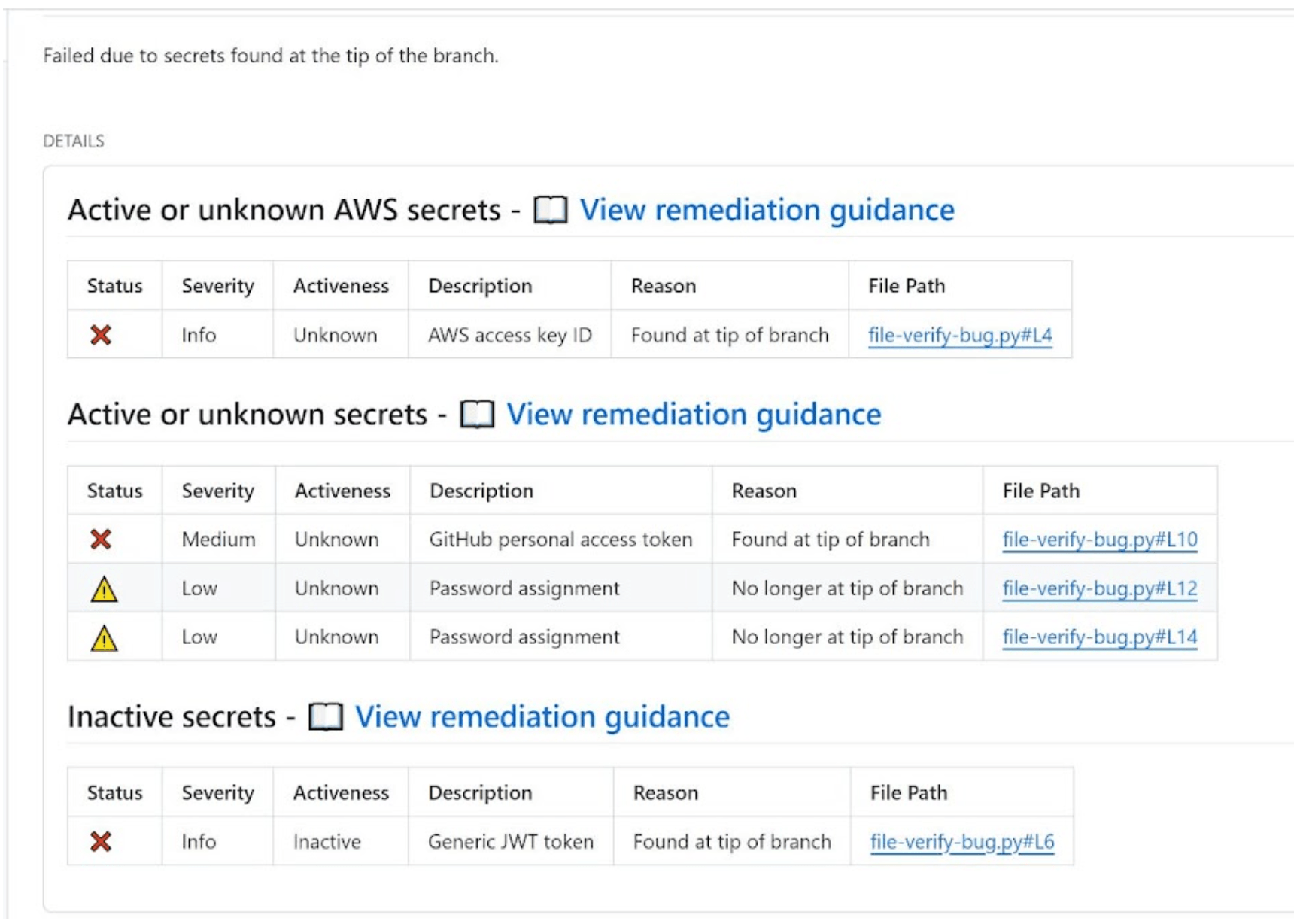
Remediation documents provide recommendations to developers based on the type of secret found in code and the secret's activeness. There are currently four provided core remediation documents.
- Active or unknown AWS secrets
- Active or unknown GCP secrets
- Active or unknown secrets (general)
- Inactive secrets
Organizations can also create their own custom remediation documents and add the link to Vault Radar to make it available in-product.
Remediation recommendations are also accessible within GitHub pull requests when using the Vault Radar GitHub App.
Remediation actions allows Vault Radar administrators to setup a connection between Radar and Vault that allows development teams to easily store leaked secrets in the correct Vault locations so they can expedite the remediation steps.
For instructions on how to set up remediation actions with Vault, read the Copy leaked secrets into HashiCorp Vault documentation.
Reducing false positives fatigue
To combat false positive fatigue, security teams should focus on improving detection engineering, tuning Vault Radar, and enhancing alert context. This involves reducing the volume of irrelevant alerts, providing more information about alerts, and automating investigations to prioritize genuine threats.
Key strategies to reduce false positive fatigue are:
- Prioritize by severity level: Focus on alerts with higher severity and potential impact, rather than overwhelming analysts with a large volume of low-priority alerts.
- Test custom regex patterns: Thoroughly test any new or modified detection rules to ensure they function as expected and don't introduce unintended consequences.
- Monitor false positives: Regularly monitor and analyze false positives to identify patterns and adjust rules accordingly, improving the overall accuracy of the scanning process.
- Exclude directories with mock data: This helps prevent Vault Radar from flagging mock data that is intentionally not sensitive.
- Manage ignore rules: The same applies for developing Global/repository specific ignore rules to reduce the flagging of findings that are not actually sensitive.